Introduction to Domain Name System
Domain names are for the benefit of humans.
IPs are difficult to remember, and if they change it is almost impossible to fully advertise the new IP to everyone. DNS maps domain names to IPs, and can advertise the services each domain offers (HTTP, MAIL, etc). This is the networking system in place that allows us to resolve human-friendly names to unique addresses. The network requests supporting DNS lookups run over TCP and UDP, port 53 by default.
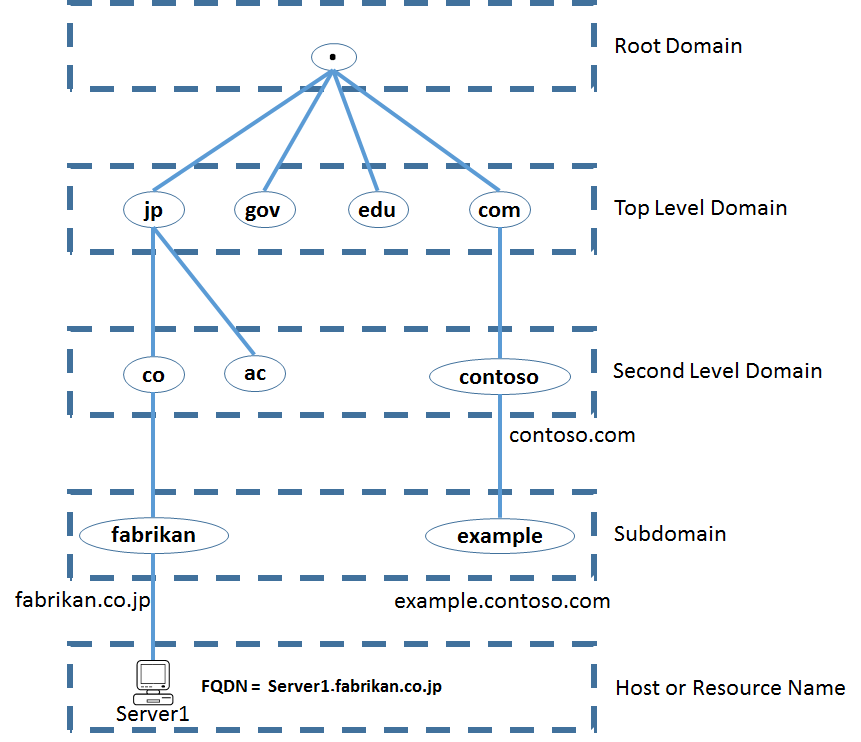
Fully Qualified Domain Name (Root-Level Domain)
FQDN - the complete, or absolute, domain name of a host, which combines the network domain with the host's name.
- mail3.example.com.
A typical domain name used to access a website is NOT an FQDN, because that domain does not reference a non-specific host, but one of several that can serve webpages for that domain.
- www.example.com may ultimately be served by webserver.example.com. or www2.example.com.
A technically correct FQDN ends with a dot as a reference to the root domain.
- Sometimes software that calls for FQDN does not require the ending dot, but the trailing dot is required to conform to ICANN standards.
Top-Level Domain
A top-level domain, or TLD, is the most general part of the domain. The top-level domain is the furthest portion to the right (as separated by a dot). Common top-level domains are "com", "net", "org", "gov", "edu", and "io".
Second-Level Domain
These are names registered to an individual or organization for use on the Internet. These names can be of Variable-length and are always based upon an appropriate top-level domain, depending on the type of organization or geographic location where a name is used.
Subdomain
Additional names that an organization can create that are derived from the registered second-level domain name. For example: "example.google.com".
Host or resource name
Typically, the leftmost label of a DNS domain name identifies a specific resource, such as a computer on the network. The difference between a host name and a subdomain is that a host defines a computer or resource, while a subdomain extends the parent domain. It is a method of subdividing the domain itself.