DNS Resolution
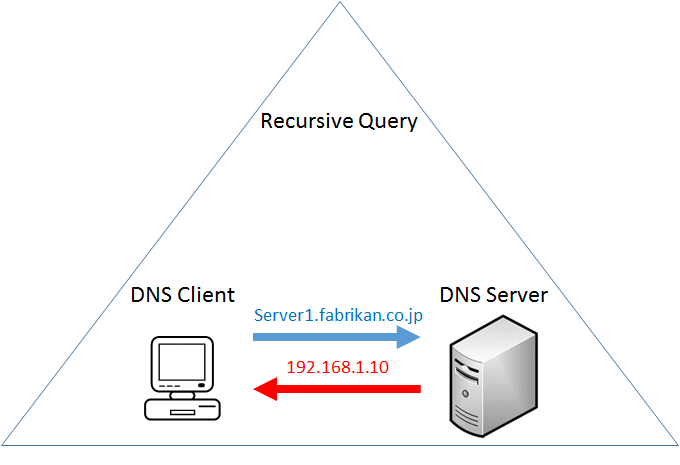
- Resolving addresses are performed with DNS Request messages.
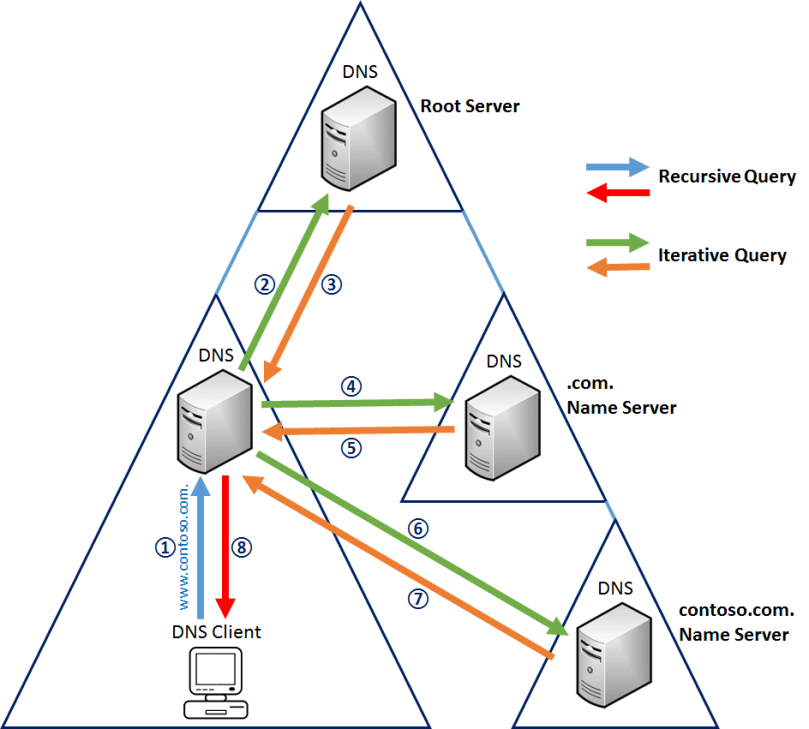
- DNS requests may be iterative or recursive. At almost every step, the cache of the current system is checked before attempting another query to reduce the load on higher servers.
- Recursive requests allow the recipient of a DNS query to make it's own DNS query. That recipient can make it's own query if needed. This is the typical method.
Iterative requests mean the host expects the DNS server to reply immediately, without asking any other DNS servers. The reply will either be from the cache, or a referral to another name server. Iterative requests may then be made by the initial host if needed.
If at any point there is a known resolution, it is passed back down immediately. No need to bother anyone else in the chain. This answer will be cached as it goes back down.