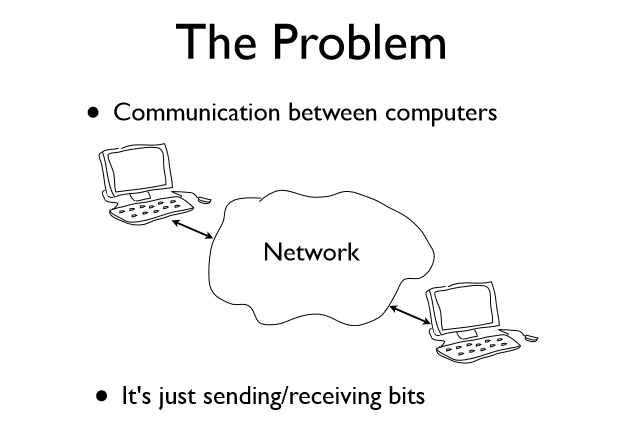
Two Main Issues
- Addressing - Specifying a remote computer and service
- Data transport - Moving bits back and forth
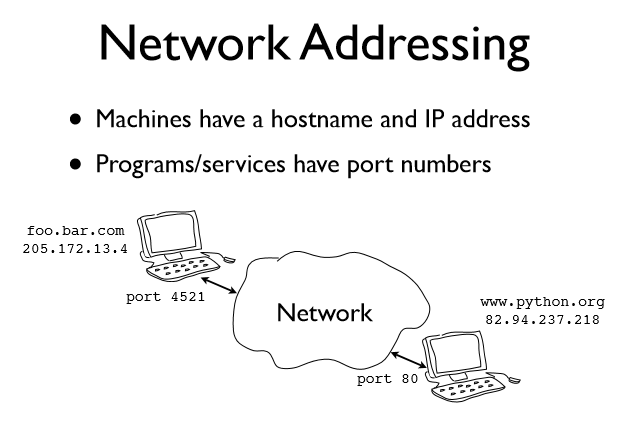
Each endpoint of a network connection is always represented by a host and port \
In Python you write it out as a tuple (host, port)
("www.python.org",80)
("205.172.13.4",443)
In all of the network programs you’ll write, you use this convention to specify a network address.
Common Ports
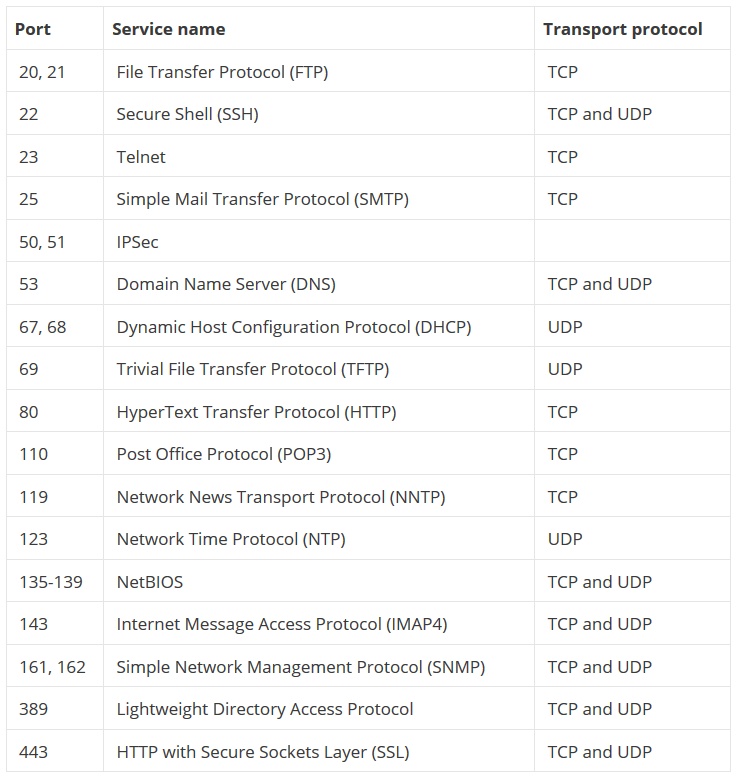
Ports are how processes get access to the network.
Port numbers < 1024 are considered "privileged" ports
Processes must have root/admin privileges to bind to these ports
They are typically reserved for servers. IANA maintains the list of well known ports
-
Ports >= 1024 can be used by anyone
If you do not bind to a port as a TCP client/UDP sender, you will get a random high number port automatically assigned to your process. This is called an “ephemeral port”.